Is 4.2 earthquake bad? GETTY A light earthquake is measured at between 4 and 4.9 on the Richter scale. Like minor quakes, they occur often worldwide, can be felt but generally cause no damage.
Also, How big was the earthquake just now in San Jose?
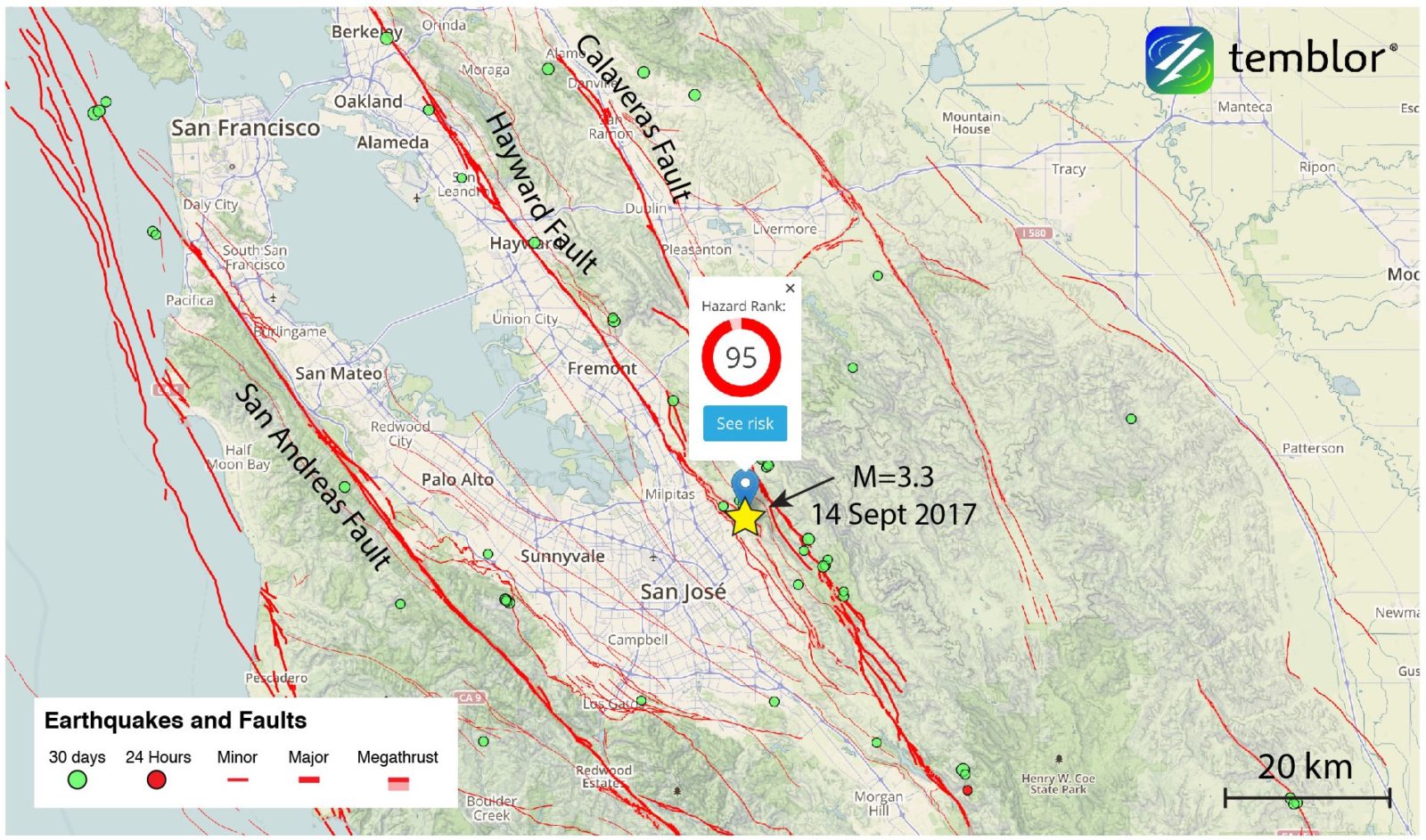
Earthquake: Magnitude 3.4 quake reported near San Jose, Calif.
Can dogs sense earthquakes? Dogs have a wider hearing range and better scent detection than humans. Some scientists suggest that dogs can hear seismic activities that precede earthquakes (such as the scraping, grinding, and breaking of rocks underground).
Is a 10.0 earthquake possible?
No, earthquakes of magnitude 10 or larger cannot happen. The magnitude of an earthquake is related to the length of the fault on which it occurs. … The largest earthquake ever recorded was a magnitude 9.5 on May 22, 1960 in Chile on a fault that is almost 1,000 miles long…a “megaquake” in its own right.
What does a 9.0 earthquake feel like?
A large earthquake far away will feel like a gentle bump followed several seconds later by stronger rolling shaking that may feel like sharp shaking for a little while. A small earthquake nearby will feel like a small sharp jolt followed by a few stronger sharp shakes that pass quickly.
Is a 3.6 earthquake bad?
Earthquakes that fall between 3.0 to 3.9 on the scale are considered minor. We can feel the earthquake, and objects inside are going to shake around, but there very rarely is damage.
Where is the San Andreas Fault?
The San Andreas Fault System, which crosses California from the Salton Sea in the south to Cape Mendocino in the north, is the boundary between the Pacific Plate (that includes the Pacific Ocean) and North American Plate (that includes North America).
How do I find out if I just had an earthquake?
Report an earthquake experience or related observation through the Did You Feel It? citizen science webpage. The best way to do this is to click on the earthquake that you think you felt on one of the lists on the Earthquakes webpage, and then select the “Tell Us!” link.
Do dogs cry before earthquake?
However, the key factor reported by dog owners who have witnessed their dogs acting out of the ordinary before an earthquake is simply any abnormal change in behavior. This could be an increase in your dog’s activity levels, heightened anxiety, barking, whining, and even trying to escape or flee.
Can snakes predict earthquakes?
For thousands of years, people have claimed that odd behavior by cats, dogs, snakes, bugs and even cows could predict an imminent earthquake, but a study — apparently the first rigorous analysis of the phenomenon — found there is no strong evidence behind the claim.
Can dogs predict death?
They provide comfort not just in death but also in other difficult times, whether it’s depression, job loss or a move across country. Dogs know when people are dying or grieving, through body language cues, smells only they can detect and other ways not yet known, experts say.
Is a 9.6 earthquake possible?
Could a magnitude 9.6 earthquake really hit San Francisco? No. Magnitude 9 earthquakes only occur on subduction zones. As stated above, there hasn’t been an active subduction zone under San Francisco or Los Angeles for millions of years.
Has there ever been a 9.9 earthquake?
The 1960 Valdivia earthquake (Spanish: Terremoto de Valdivia) or the Great Chilean earthquake (Gran terremoto de Chile) on 22 May 1960 was the most powerful earthquake ever recorded.
…
1960 Valdivia earthquake.
| Iquique Santiago Punta Arenas | |
|---|---|
| UTC time | 1960-05-22 19:11:14 |
| Casualties | 1,000–6,000 |
Can San Andreas really happen?
No. The San Andreas is actually mostly on land. Big tsunamis are created by faults underwater. … So even when the San Andreas goes underwater, “it doesn’t move the ocean floor up or down very much,” Jordan said, which is needed to create a big tsunami.
What would a 20.0 earthquake do?
A magnitude 20 earthquake would produce more than enough energy to overcome the gravitational binding energy and destroy our planet. But the good news is that we would likely see the massive asteroid coming and would have time to prepare for everything that comes with it.
Is Cascadia possible?
Seven times in the past 3,500 years, the CSZ has buckled and fractured to produce an earthquake so massive that it left a mark in the geologic record. There’s a one-in-10 chance that the next major Cascadia quake will occur sometime in the next 50 years. The odds of a lesser but still major event are even greater.
What is a phantom quake?
Real aftershocks are possible after big earthquakes — but imagined ones can happen, too. … “Aside from aftershocks, anyone caught up in the disaster may also experience the uncanny sensation of ‘phantom quakes,’ where it feels as if the earth is shaking when, in fact, it is perfectly still,” Glaser wrote.
What would a 10.0 earthquake do?
A magnitude 10 quake would likely cause ground motions for up to an hour, with tsunami hitting while the shaking was still going on, according to the research. Tsunami would continue for several days, causing damage to several Pacific Rim nations.
How bad is a 7.2 earthquake?
Learn more about how we measure earthquake magnitude.
…
Earthquake Magnitude Scale.
| Magnitude | Earthquake Effects | Estimated Number Each Year |
|---|---|---|
| 7.0 to 7.9 | Major earthquake. Serious damage. | 10-15 |
| 8.0 or greater | Great earthquake. Can totally destroy communities near the epicenter. | One every year or two |
Does the San Andreas Fault run through Mexico?
The San Andreas Fault is the sliding boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. It slices California in two from Cape Mendocino to the Mexican border.
Can the San Andreas Fault cause a 9.0 earthquake?
The San Andreas fault is not long and deep enough to have a magnitude 9 or larger earthquake as depicted in the movie. … Computer models show that the San Andreas fault is capable of producing earthquakes up to about magnitude 8.3.
Can San Andreas really happen?
Yes. In the San Andreas movie, a 9.6 magnitude earthquake hits San Francisco, which was triggered by a 9.1 magnitude quake in Los Angeles, following a 7.1 in Nevada. U.S. Geological Survey seismologist Dr. … In 1992, a 7.3 quake hit Southern California and triggered a 5.7 in Nevada (NPR.org).











Leave a Review