Can you dream during g lock? Upon regaining cerebral blood flow, the G-LOC victim usually experiences myoclonic convulsions (often called the ‘funky chicken’) and often full amnesia of the event is experienced. Brief but vivid dreams have been reported to follow G-LOC.
Also, Why do pilots pass out from g-force?
Fighter pilots lose consciousness or blackout when they pull a High-G maneuver in their aircraft which forces all the blood from their brain and into the abdomen and feet. Without blood delivering oxygen to the brain, it can cause unconsciousness within 5-10 seconds at 4g and higher.
How many G’s can a human take? Normal humans can withstand no more than 9 g’s, and even that for only a few seconds. When undergoing an acceleration of 9 g’s, your body feels nine times heavier than usual, blood rushes to the feet, and the heart can’t pump hard enough to bring this heavier blood to the brain.
How many G’s is lethal?
Changes in speed are expressed in multiples of gravitational acceleration, or ‘G’. Most of us can withstand up to 4-6G. Fighter pilots can manage up to about 9G for a second or two. But sustained G-forces of even 6G would be fatal.
What does 7g force feel like?
The speed stabilizes and the G meter reads 7.0. You continue the G strain, but your body is in pain. Not only does it feel like being smothered by really heavy weights, but every inch of your body feels as if it is under a vise. The pain is overbearing, but you have to hang on.
How do female fighter pilots go to the bathroom?
They are specially shaped bags with absorbent beads in them. If we have to relieve ourselves, we’ll unzip the flight suit—which is designed to unzip from the top as well as the bottom—unroll the piddle pack, and then pee into it.
Do fighter pilots get brain damage?
Aviators piloting aircraft at very high altitudes for the military have “significantly more” brain lesions known as white matter hyperintensities, US Air Force medical researchers have found through MRI scanning.
What does 9 G’s feel like?
It’s similar to a bruise and usually dissipates within a few days. The long term effects of high-G’s can result in neck and back issues—most pilots deal with some level of general pain due to G’s. With our helmets on, over 135 pounds of force is applied to the neck at 9G’s.
Why does g-force make you sick?
This is because the g-force is pulling the ribs down, which empties the air from the lungs. This isn’t the most dangerous effect, but it does wear you out. The most dangerous effect is that blood is pulled away from the brain and pools in the legs and feet. … It is called a g-LOC (g-induced Loss Of Consciousness).
What is negative g-force?
Negative G forces are the opposite of positive G’s. These occur when cresting a hill on a roller coaster. Anything below one G is considered a negative G. … Roller coaster enthusiasts call it air time. Essentially, negative G’s are a resistance of a force of gravity, since your moving upwards, not down.
How fast is 1 g in mph?
For example: An acceleration of 1 g equates to a rate of change in velocity of approximately 35 kilometres per hour (22 mph) for each second that elapses.
What is the most g’s ever pulled?
There are isolated incidents of humans surviving abnormally high G-forces, most notably the Air Force officer John Stapp, who demonstrated a human can withstand 46.2 G’s. The experiment only went on a few seconds, but for an instant, his body had weighed over 7,700 pounds, according to NOVA.
What is 9 G’s of force?
Modern fighters like the F-16 and F-35 pull 9G’s, which translates to over 2,000 pounds on my body. Under 9G’s, the world appears to shrink until it looks like you’re viewing it through a toilet paper roll. Blood is being pulled out of your head towards your legs and arms, resulting in the loss of peripheral vision.
Is G force painful?
It’s similar to a bruise and usually dissipates within a few days. The long term effects of high-G’s can result in neck and back issues—most pilots deal with some level of general pain due to G’s. With our helmets on, over 135 pounds of force is applied to the neck at 9G’s.
How do fighter pilots handle G force?
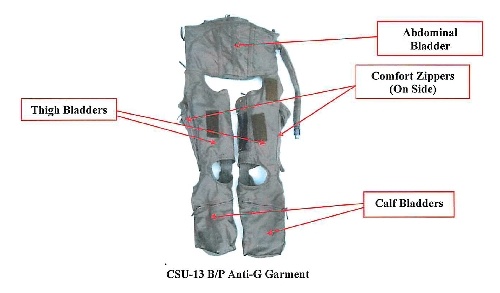
Fighter pilots can handle greater head-to-toe G forces—up to 8 or 9 G’s—and for longer periods by wearing anti-G suits. These specialized outfits use air bladders to constrict the legs and abdomen during high G’s to keep blood in the upper body.
Do pilots have guns?
Thousands of US airline pilots carry guns in the cockpit. Why do they do it – and how are they trained? … A year later, the Arming Pilots Against Terrorism Act was passed, allowing US pilots – working for US airlines – to carry guns in the cockpit.
Do jet pilots wear diapers?
Piddle Packs are small bags male fighter pilots use to pee while in flight. … They are specially shaped bags with absorbent beads in them. If we have to relieve ourselves, we’ll unzip the flight suit—which is designed to unzip from the top as well as the bottom—unroll the piddle pack, and then pee into it.
Why do planes do not fly over the Pacific?
The primary reason airplanes don’t fly over the Pacific Ocean is because curved routes are shorter than straight routes. Flat maps are somewhat confusing because the Earth itself isn’t flat. Rather, it’s spherical. As a result, straight routes don’t offer the shortest distance between two locations.
Do Air Force pilots get PTSD?
Most people don’t think about PTSD among aviators, whether they are pilots, air crew, door gunners, first aid personnel, medics, or corpsman. … However, aviators can still develop PTSD due to their line of work.
Can a pilot have Parkinson’s?
Pilots are certificated annually and asked to provide a status report from treating physicians each year for continued certification. For pilots flying under BasicMed, Parkinson’s disease is not one of the 11 conditions that require a one-time special issuance medical certificate.
How does altitude sickness affect a fighter pilot?
High-altitude pilots are at increased risk of decompression sickness, or “the bends,” in which decreasing pressure allows bubbles of gas to form in the blood and can lead to temporary slowed mental processing or permanent cognitive decline.











Leave a Review